Expose Application Service Deployed on CSP Kubernetes
Deploying application on the Kubernetes provided by CSP (Cloud Service Provider) is convenient and reliable, which is adopted by many enterprises. Kusion has a good integration with CSP Kubernetes service. You can deploy your application to the Kubernetes cluster, and expose the service in a quite easy way.
This tutorial demonstrates how to expose service of the application deployed on CSP Kubernetes. And the responsibilities of platform engineers and application developers are also clearly defined. In this article, exposing the service of nginx (referred to "the example" in the below) is given as an example.
Prerequisites
Create a Kubernetes cluster, the following CSP Kubernetes services are supported.
Expose Service Publicly
If you want the application can be accessed from outside the cluster, you should expose the service publicly. Follow the steps below, you will simply hit the goal.
Set up Workspace
Create the workspace as the target where the application will be deployed to. The workspace is usually set up by platform engineers, which contains platform-standard and application-agnostic configurations. The workspace configurations are organized through a YAML file.
modules:
port:
default:
type: alicloud
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-spec: slb.s1.small
runtimes:
kubernetes:
kubeconfig: "<your kube-config file path>"
The YAML shown above gives an example of the workspace configuration to expose service on ACK. The file contains two top-level blocks modules and runtimes, and the block port under modules, kubernetes under runtimes.
The block port contains the workspace configuration of module port, which has the following fields:
- type: the CSP providing Kubernetes service, support
alicloudandaws - annotations: annotations attached to the service, should be a map
- labels: labels attached to the service, should be a map
The block kubernetes contains the kubernetes related configuration, which has the following fields:
- kubeconfig: the kube-config file path, which is got after creating the cluster.
You can also configure kube-config by environment variables, which has higher priority.
export KUBE_CONFIG="<kube-config file>"
Then, create the workspace with the configuration file. Be attention, the workspace name must be the same as the stack name. The following command creates a workspace named dev with configuration file workspace.yaml.
kusion workspace create prod workspace.yaml
Write Configuration Code
After creating workspace, you should write application configuration code, which only contains simple and application-centric configurations. This step is usually accomplished by application developers.
import catalog.models.schema.v1 as ac
import catalog.models.schema.v1.workload as wl
import catalog.models.schema.v1.workload.container as c
import catalog.models.schema.v1.workload.network as n
nginx: ac.AppConfiguration {
workload: wl.Service {
containers: {
nginx: c.Container {
image = "nginx:1.25.2"
resources: {
"cpu": "500m"
"memory": "512Mi"
}
}
}
replicas: 1
ports: [
n.Port {
type: "aliyun"
port: 80
protocol: "TCP"
public: True
}
]
}
}
The code shown above describes how to expose service publicly on ACK. Kusion use schema Port to describe the network configuration, the primary fields of Port are as follows:
- port: port number to expose service
- protocol: protocol to expose service, support
TCPandUDP - public: whether to public the service
To public the service, you should set public as True. Besides, schema Service should be used to describe the workload configuration.
That's all what an application developer need to configure! Next, preview and apply the configuration, the application will get deployed and exposed publicly.
Kusion uses Load Balancer (LB) provided by the CSP to expose service publicly. For more detailed network configuration, please refer to Application Networking
Preview and Apply
Execute kusion preview under the stack path, you will get what will be created in the real infrastructure. The picture below gives the preview result of the example. A Namespace, Service and Deployment will be created, which meets the expectation. The service name has a suffix public, which shows it can be accessed publicly.
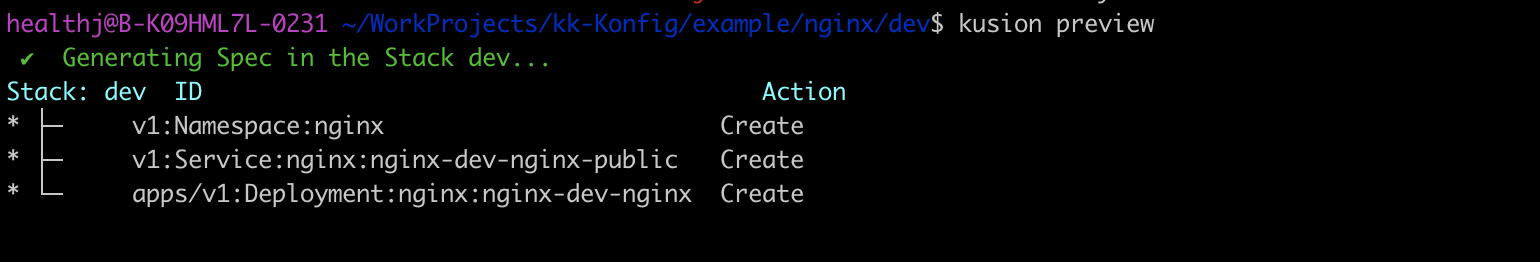
Then, execute kusion apply --yes to do the real deploying job. Just a command and a few minutes, you have accomplished deploying application and expose it publicly.
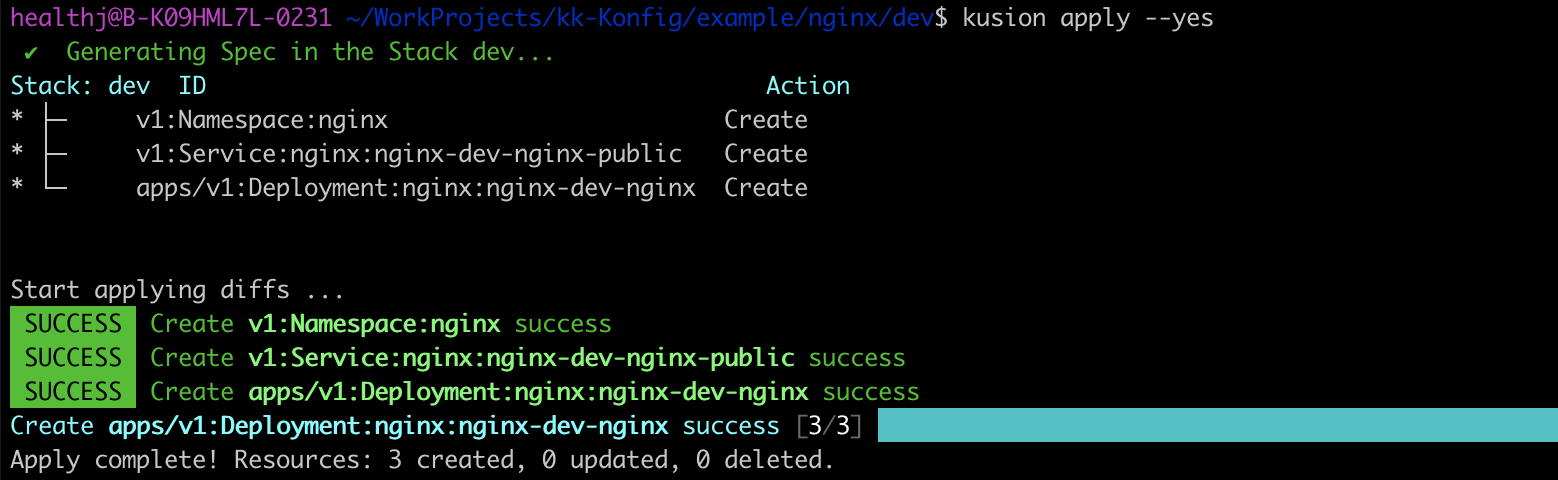
Verify Accessibility
In the example, the kubernetes Namespace whose name is nginx, and a Service and Deployment under the Namespace should be created. Use kubectl get to check, the Service whose type is LoadBalancer and Deployment are created indeed. And the Service has EXTERNAL-IP 106.5.190.109, which means it can be accessed from outside the cluster.
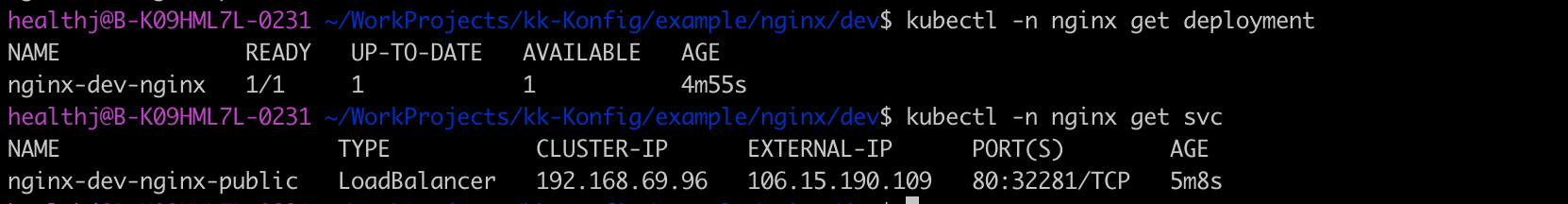
Visit the EXTERNAL-IP via browser, the correct result is returned, which illustrates the servie get publicly exposed successfully.
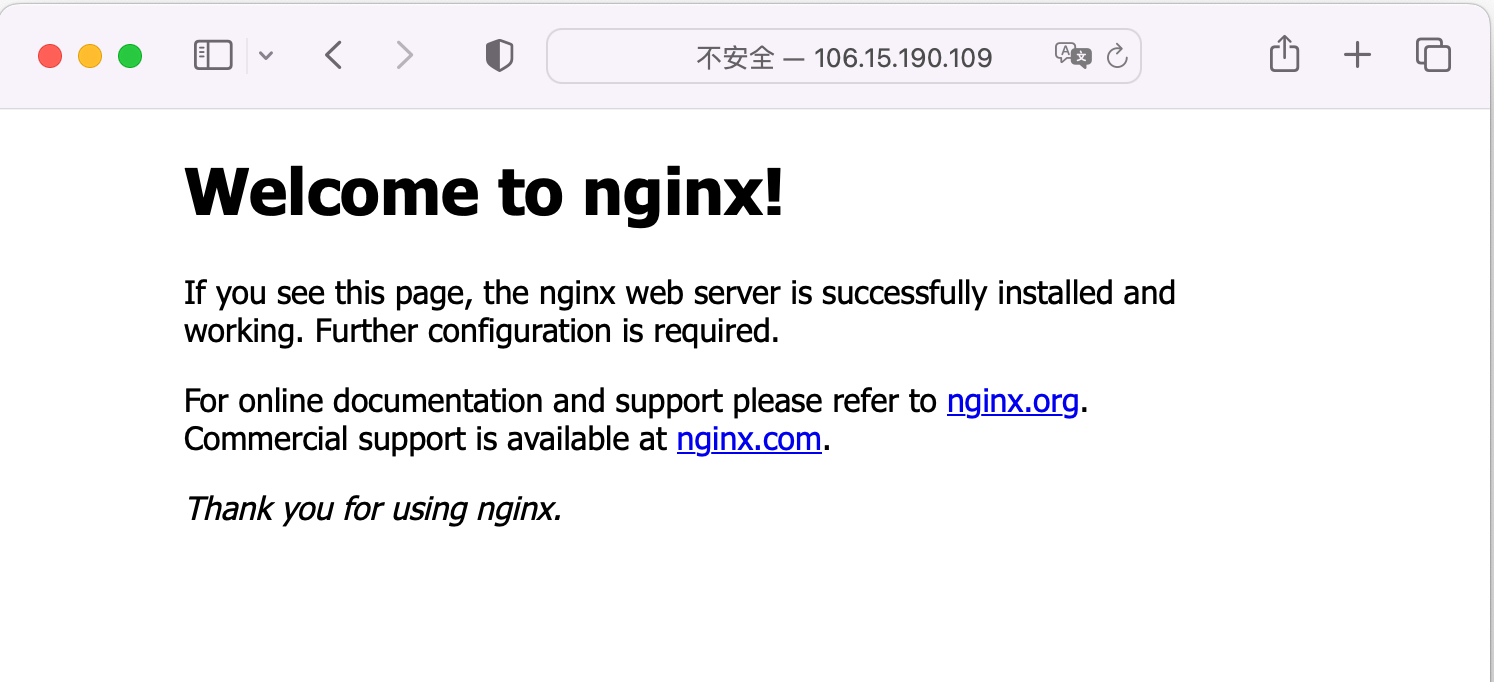
Expose Service Inside Cluster
If you only need the application can be accessed inside the cluster, just configure Public as False in schema Port. There is no need to change the workspace, which means an application developer can easily change a service exposure range, without the involvement of platform engineers.
import catalog.models.schema.v1 as ac
import catalog.models.schema.v1.workload as wl
import catalog.models.schema.v1.workload.network as n
nginx: ac.AppConfiguration {
workload: wl.Service {
...
ports: [
n.Port {
...
public: False
}
]
}
}
Execute kusion apply --yes, the generated Service has suffix private.
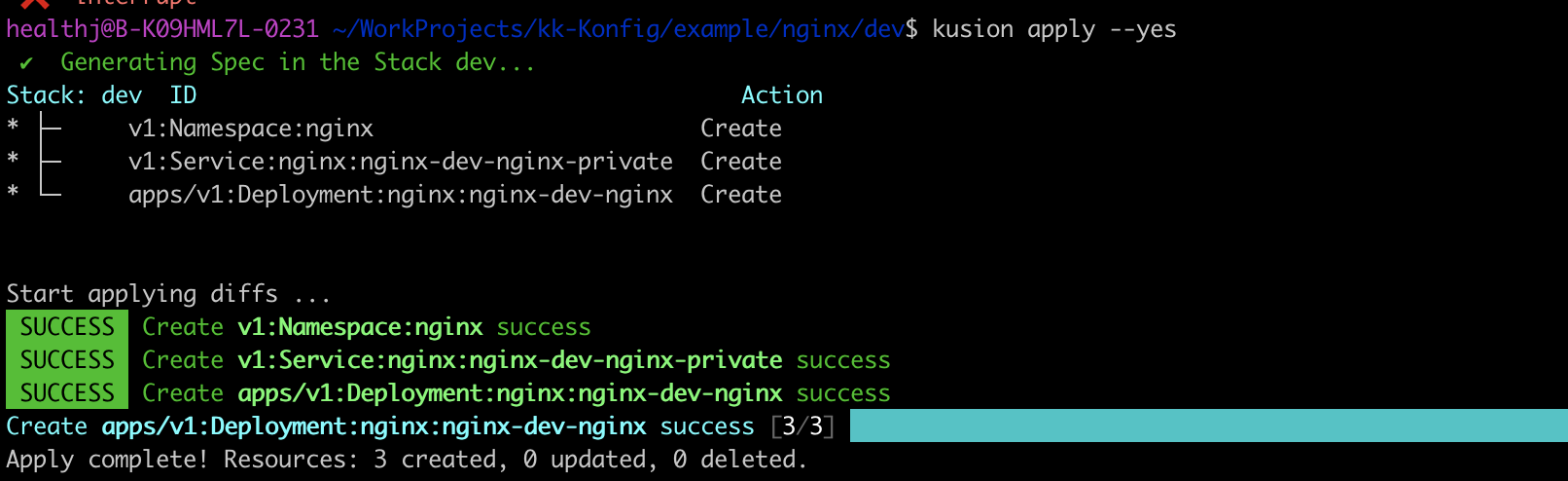
And the Service type is ClusterIP, only has CLUSTER_IP and no EXTERNAL_IP, which means it cannot get accessed from outside the cluster.

Summary
This tutorial demonstrates how to expose service of the application deployed on the CSP Kubernetes. By platform engineers' setup of workspace, and application developers' configuration of schema Port, Kusion enables you expose service simply and efficiently.